How to Fix the “Site Can’t Be Reached” Error: Complete Guide
September 18, 2025 by Benjamin
Uncategorized
September 18, 2025 by Benjamin
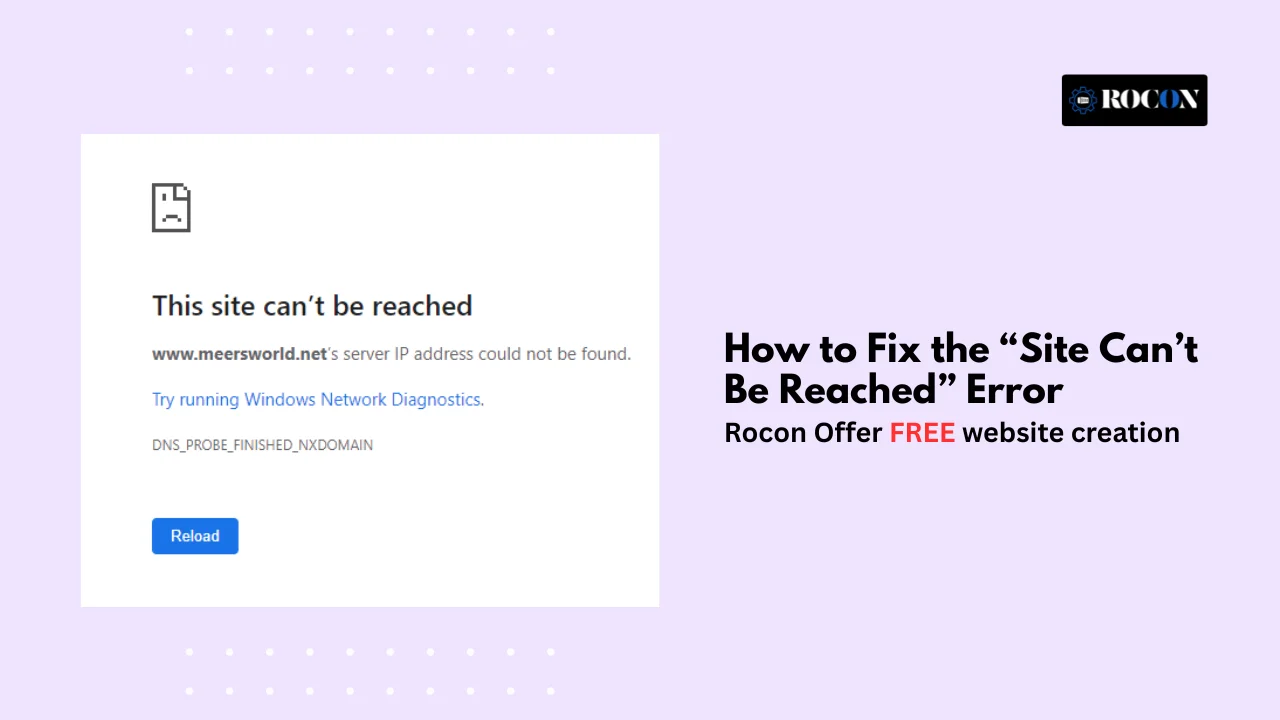
Few things are more frustrating than typing in a web address, hitting enter, and staring at the dreaded message: “This site can’t be reached.” If you’re a regular internet user, it feels like hitting a brick wall. If you’re a WordPress site owner, it’s even worse — potential visitors and customers are locked out, and you might not even know why.
The good news? This error isn’t the end of the world. It’s usually something small — a setting is misconfigured, a network issue or a WordPress problem. In this post we’ll go into what the error means, why it happens and step by step solutions from the simple fixes to advanced troubleshooting. By the end you’ll not only fix the problem but also know how to prevent “site can’t be reached” from happening again.
At its core, the “This site can’t be reached” message is a catch-all error displayed by browsers (Chrome, Edge, Firefox, etc.) when they fail to connect to a website. Instead of giving a detailed explanation, the browser shows this generic message, which can be triggered by several underlying issues.
When the browser shows this message, it often comes with specific error codes that provide clues:
Each of these codes tells a slightly different story, and identifying them is the first step to troubleshooting.
To solve this error, it’s important to distinguish whether the issue is on your device/network (client-side) or the website’s hosting/server (server-side).
Once you know which side the issue is on, you can apply the right fix without wasting time.
The “This site can’t be reached” message can feel vague, but the root causes usually fall into a handful of categories. Let’s unpack the most common ones so you can start narrowing down where the problem lies.
DNS (Domain Name System) is like the internet’s phonebook. When you type in a domain (e.g., example.com), DNS translates it into an IP address that browsers can connect to. If DNS fails, your site won’t load.
Symptom: Usually paired with DNS_PROBE_FINISHED_NXDOMAIN.
Sometimes the problem isn’t the site or domain at all—it’s your network.
Symptom: Site loads fine on another network (e.g., switching from WiFi to mobile data).
Browsers themselves can cause trouble if local data or settings interfere with connections.
Symptom: Error disappears when testing in another browser or in incognito mode.
If the client side looks fine, the culprit may be the server hosting the WordPress site.
Symptom: Error appears for everyone across all devices and networks.
Because we’re focusing on WordPress, it’s important to highlight issues unique to WP environments.
Symptom: The error appears right after a WordPress update, plugin activation, or SSL setup.
Finally, sometimes the issue lives entirely on the user’s device.
Symptom: Only one device in your household/workplace can’t access the site.
Troubleshooting a “This site can’t be reached” error becomes much easier if you start by gathering evidence instead of blindly trying fixes. Here are the most effective ways to narrow down the cause:
First, check whether the problem is isolated to one device or network.
Why this matters: This step instantly tells you whether to focus on client-side fixes or server-side investigation.
The browser error code is your biggest clue.
Take note of the exact code—it saves you from unnecessary troubleshooting.
If the issue points to DNS, verify the domain setup.
If DNS looks inconsistent worldwide, it’s either propagation delay or misconfigured DNS records.
For site owners, the next step is checking the hosting environment.
Example: If the logs show repeated PHP fatal errors, the issue is WordPress-related rather than DNS.
For advanced users, the browser itself provides diagnostic tools.
Helpful when the site partially loads but fails to fetch certain resources.
If you’re the site owner and can still access the backend:
This often points directly to faulty plugins, themes, or misconfigured WordPress URLs.
If you’re just trying to access a website and keep running into the “This site can’t be reached” error, start with these fixes. They address the most common client-side issues like network, browser, or DNS problems.
Sometimes the simplest fix is the most effective.
Why it works: Routers often cache DNS or get stuck in a bad state, and a reset clears it.
Switch to another network to rule out ISP or local WiFi issues.
If the site loads elsewhere, the issue is with your local ISP or router.
Corrupted cache or cookies can block websites.
If clearing cache fixes the problem, your browser was holding onto outdated or corrupted files.
Security software sometimes blocks legitimate sites by mistake.
If disabling works, whitelist the site in your antivirus/firewall settings.
DNS cache stores IP addresses of websites, but if outdated, it can block access.
Windows: Open Command Prompt and type:
ipconfig /flushdns
macOS: In Terminal, type:
sudo dscacheutil -flushcache; sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder
This forces your system to fetch fresh DNS records.
If your ISP’s DNS is unreliable, switch to a public DNS for faster, more stable browsing.
This fix alone resolves a large percentage of DNS_PROBE_FINISHED_NXDOMAIN errors.
A faulty proxy or unstable VPN tunnel can block connections.
If the site works without VPN/proxy, the issue is routing-related.
If none of the above work, reset all network configurations to factory defaults.
This wipes out problematic configurations and gives you a fresh start.
These fixes cover 90% of cases where a visitor encounters the “This site can’t be reached” error. If the site still won’t load after trying them, chances are the problem lies on the server or WordPress side—something only the site owner can fix.
Now let’s get into territory most generic guides skip: WordPress-related reasons for “site can’t be reached.” Even if your domain and server are fine, certain WordPress settings or files can break the connection. Here are the biggest culprits:
If you’ve confirmed that the issue isn’t on the visitor’s end, it’s time to investigate your WordPress hosting environment and site configuration. Here are the most effective steps to bring your site back online.
Your site won’t load if the domain itself isn’t pointing correctly.
Pro tip: Use WhatsMyDNS to confirm global DNS resolution.
Sometimes the server is simply down or overloaded.
If you can SSH into the server, run:
uptime
top
to see server load.
If the server itself is unreachable, contact your hosting provider.
If the issue happens only on HTTPS, your SSL setup may be broken.
Expired SSL certificates are one of the most common reasons users see ERR_SSL_PROTOCOL_ERROR.
Faulty or incompatible plugins/themes can prevent WordPress from loading.
Always test plugins/themes in a staging environment before updating.
A corrupted .htaccess file can block connections.
Nginx users should check their server block configuration instead.
If site_url or home_url values are incorrect, WordPress won’t load properly.
If you can’t access Admin, update directly in the database:
UPDATE wp_options SET option_value=’https://yourdomain.com’ WHERE option_name=’siteurl’ OR option_name=’home’;
Or update via wp-config.php by adding:
define(‘WP_HOME’,’https://yourdomain.com’);
define(‘WP_SITEURL’,’https://yourdomain.com’);
Misconfigured URLs often happen after migrations or SSL installations.
If WordPress can’t connect to its database, it may show as unreachable.
If credentials are wrong, WordPress won’t establish a connection, leading to downtime.
If your site is under heavy load, scripts may time out before completing.
In wp-config.php, add:
define(‘WP_MEMORY_LIMIT’, ‘256M’);
In php.ini (if accessible), adjust:
memory_limit = 256M
max_execution_time = 300
This helps prevent ERR_TIMED_OUT or ERR_CONNECTION_RESET errors.
Logs are the ultimate truth tellers.
Example: A recurring “Allowed memory size exhausted” error means you need to raise PHP limits.
If you use Cloudflare or another CDN, issues at their end can cause outages.
If disabling the CDN fixes the issue, the problem is external, not with your WordPress server.
By following these steps, WordPress site owners can systematically eliminate common causes of the “This site can’t be reached” error on the server side.
For those comfortable with a bit of technical digging, these tools can reveal exactly where the connection is breaking:
Ping: Tests whether the server is reachable.
ping yourdomain.com
Traceroute: Shows the path between your device and the server. Useful for spotting ISP or routing issues.
tracert yourdomain.com (Windows)
traceroute yourdomain.com (Mac/Linux)
Nslookup / Dig: Check DNS records directly.
nslookup yourdomain.com
dig yourdomain.com
Run:
curl -I https://yourdomain.com
This shows the HTTP response headers. A 200 response = good; 500/502/504 = server issue.
These tools go beyond “try restarting your router.” They help you pinpoint whether the issue is local, network-related, or server-side.
Sometimes, “site can’t be reached” appears under very specific conditions. Let’s cover those competitors often miss:
Fixing the error is one thing — preventing it is where true peace of mind lies. Here’s how to reduce the chances of “site can’t be reached” happening again:
The “site can’t be reached” error is scary, especially when it’s your WordPress site on the line. But it’s a fixable problem once you know where to look. From quick user fixes like clearing cache and flushing DNS to deeper WordPress fixes like SSL or .htaccess the solutions are in your hands.
And by putting preventive measures in place — reliable DNS, SSL auto-renewal, uptime monitoring, and managed hosting — you’ll drastically reduce the chance of seeing this error again. Next time your site refuses to load, you’ll know exactly how to turn frustration into a fix.
Elevate your WordPress hosting with 30-day money-back guarantee, free migration, and 24/7 support.
Sign Up TodayMarch 6, 2026
Akshay
9 Min Read
March 4, 2026
Maria
7 Min Read
February 27, 2026
Srilatha
10 Min Read
Before You Go… Get 1 Month FREE on Rocon Hosting!
Experience lightning-fast speeds
No downtime or hidden fees
Dedicated 24/7 expert support

Our team will contact you soon.




Leave a Reply